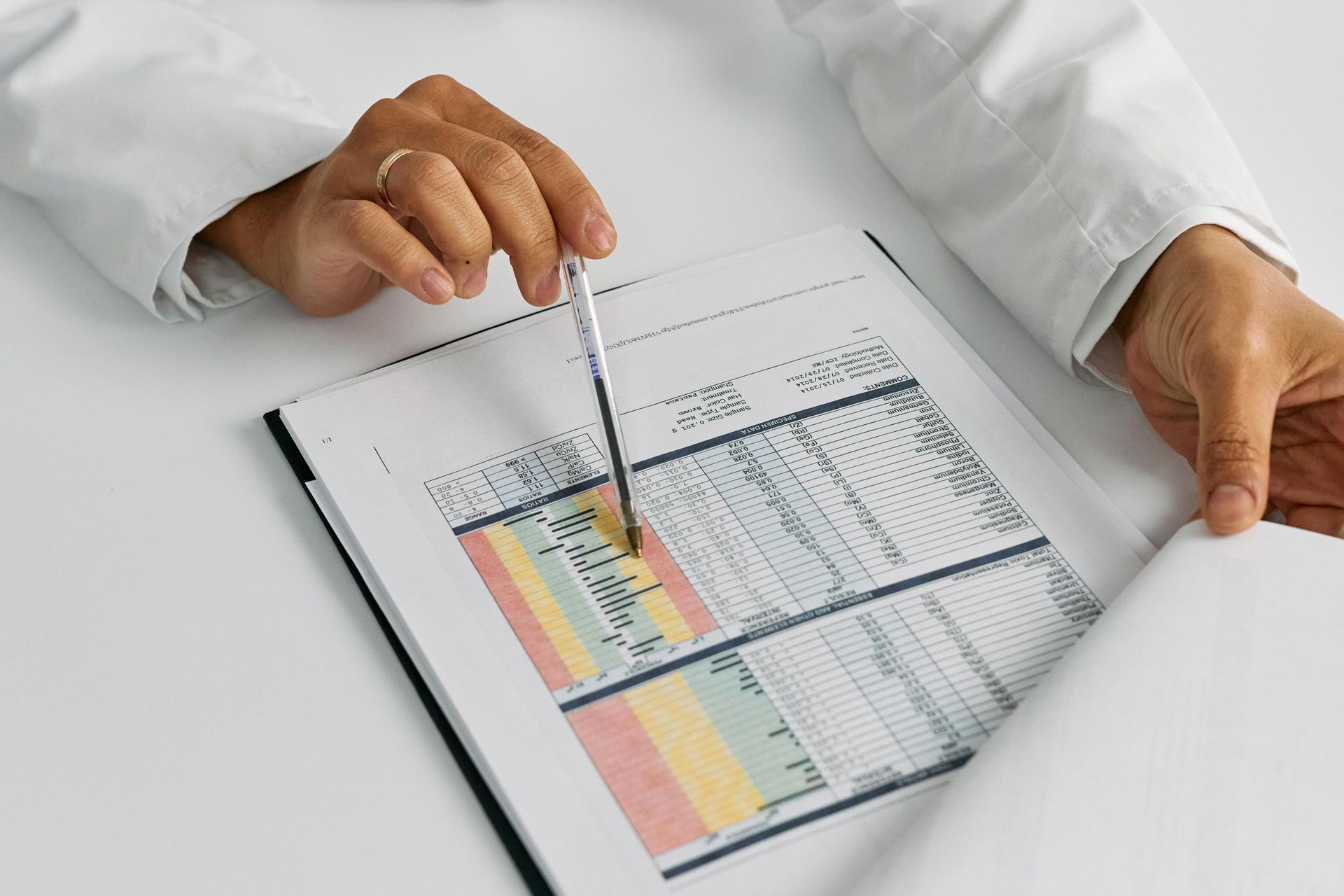
Understanding Your Labs
100% Online Therapy
1. Choose Your Treatment
Plan

Select the therapy that aligns with your health goals and lifestyle.
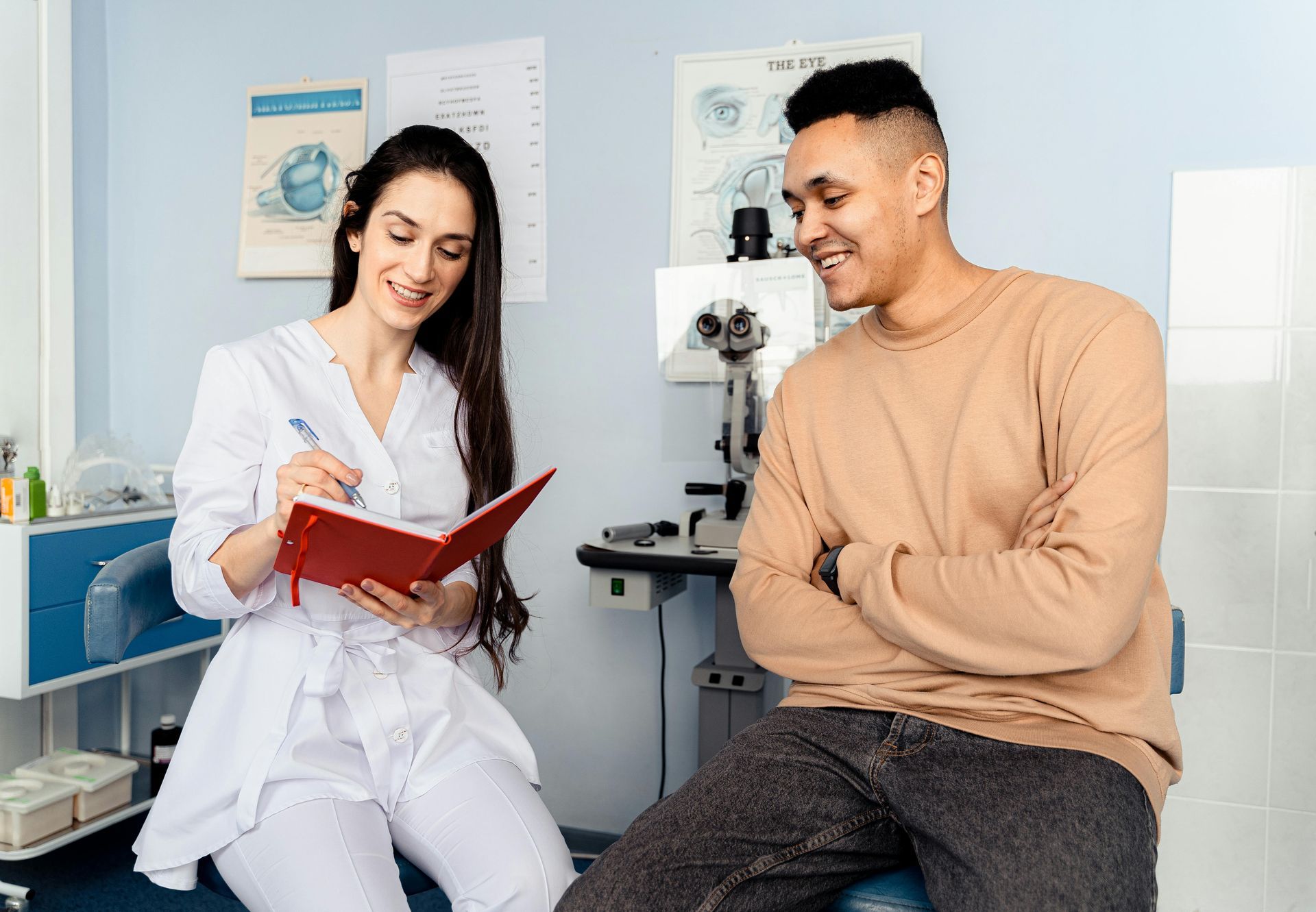
2. Review Your Lab Results
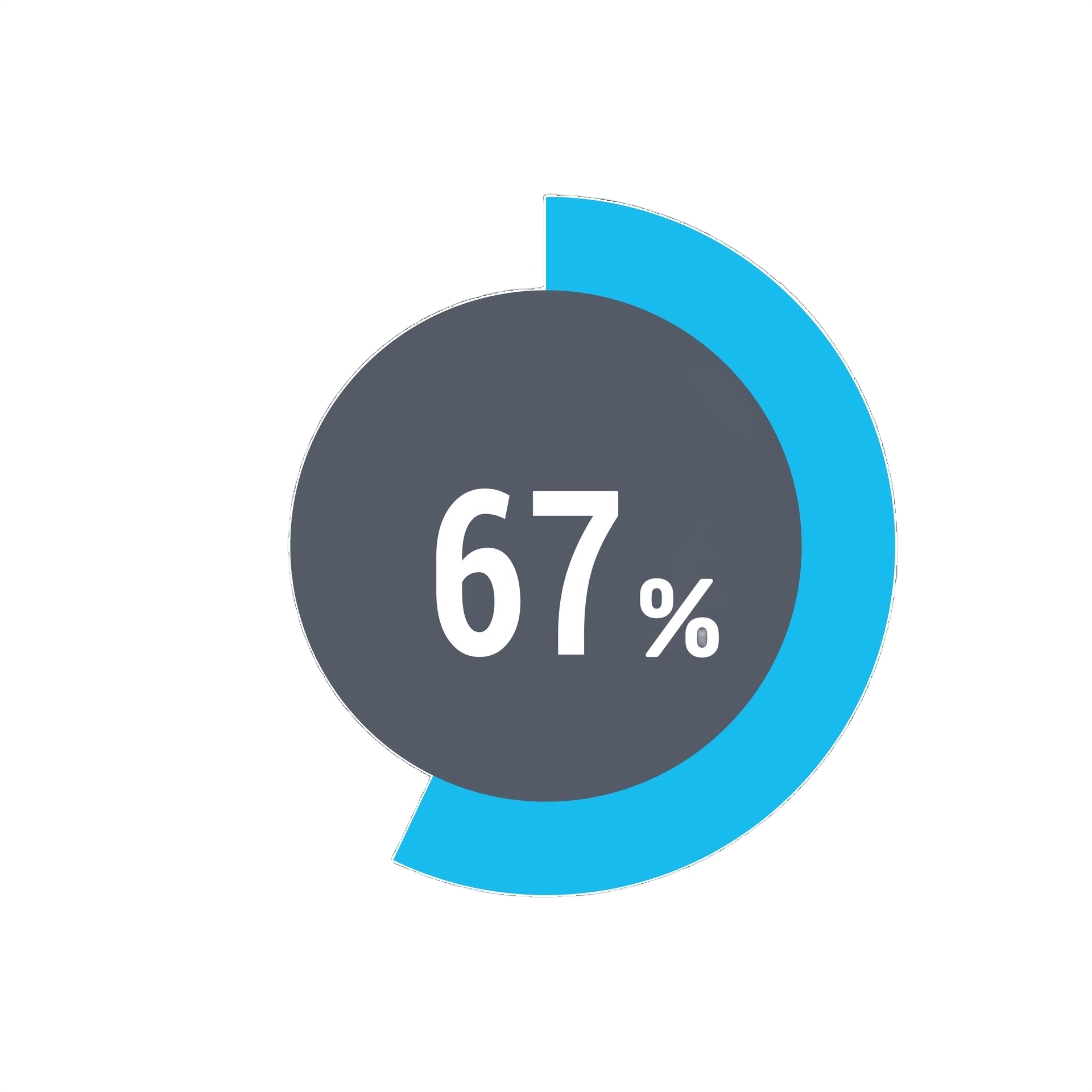
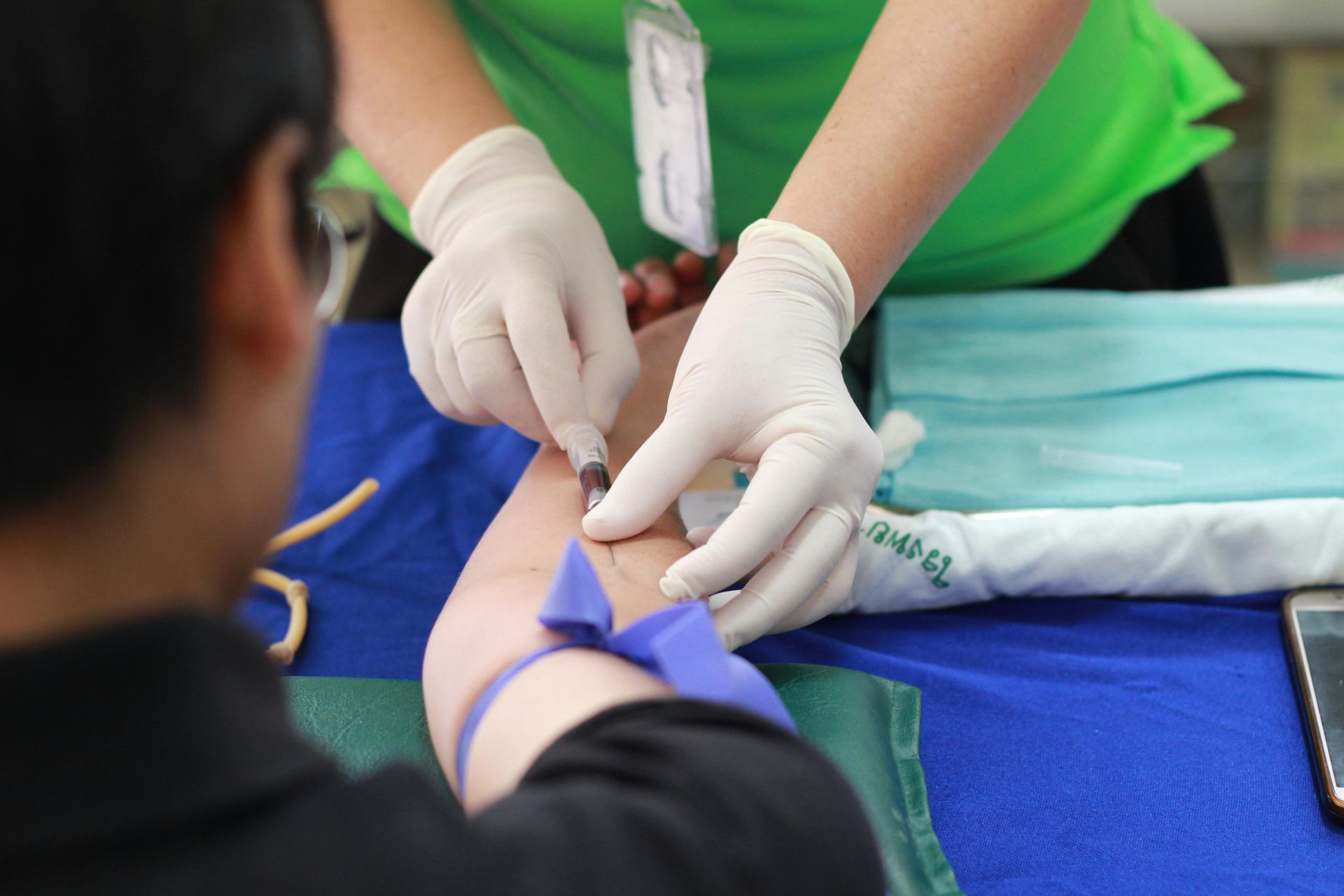
Upload recent lab work or conveniently order fast, external labs, we'll provide you a lab requisition.
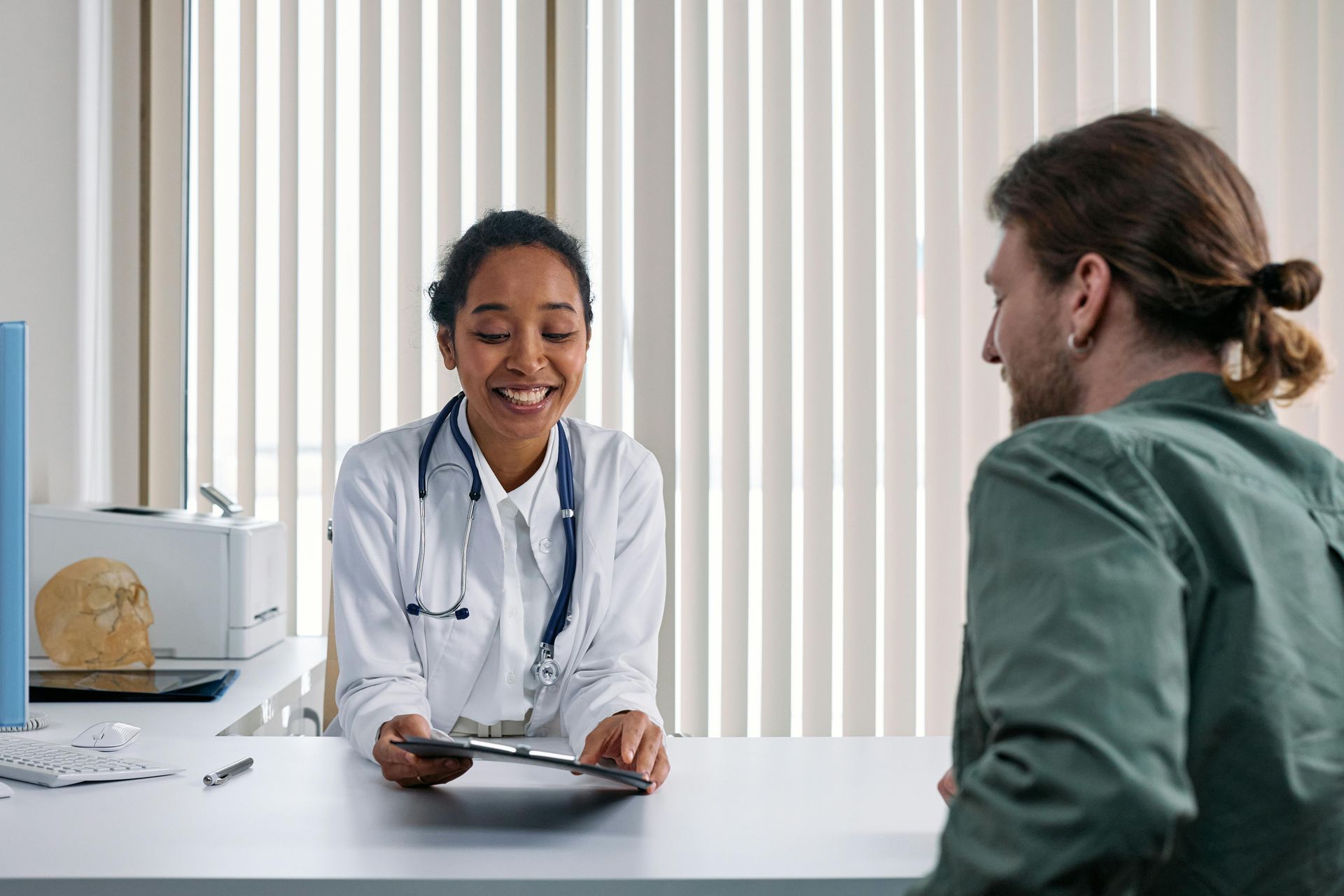
3. Consult With a Licensed Provider

Receive one-on-one, personalized care as you discuss your symptoms, goals, and treatment options.
4. Start Your Customized Treatment

Your prescribed therapy is prepared and delivered discreetly to your door.
🩸 Hemoglobin & Hematocrit
Effect of TRT: Testosterone signals your kidneys to release erythropoietin (EPO), which stimulates bone marrow to produce more red blood cells. This can improve mild anemia and boost energy.
Safety Concern: If Hb/Hct rise too high, blood becomes “thicker.”
Monitoring Steps:
- Baseline testing before therapy
- Check‑ins at 8 weeks, then every 6 months
- Management if levels rise too high
- Therapeutic phlebotomy (similar to donating blood) lowers Hb/Hct safely

🧬 LH & FSH
Why test before TRT: Identifies the root cause of low testosterone.
- Primary hypogonadism: LH/FSH high, testes not responding → TRT is standard treatment.
🧪 PSA (Prostate‑Specific Antigen)
Purpose: Protein from prostate cells, key for prostate health monitoring.
Before TRT: Establish a baseline PSA to detect pre‑existing conditions like
BPH.
During TRT: PSA may rise slightly. Concern is a rapid or significant increase.
Monitoring:
- Test every 6 months
- Refer to urology if PSA rises substantially

💪 Total vs Free Testosterone
Total Testosterone (TT): Measures all testosterone (bound + free).
Free Testosterone (FT): The active hormone available to cells.
Why check both:
- Normal TT but low FT can still cause symptoms
- Borderline TT clarified by FT
- Monitoring both ensures safe, effective TRT
⚖️ Estradiol Balance
Why it rises on TRT: More testosterone → more conversion to estradiol via aromatase.
Role in men:
- Maintains bone density & cardiovascular health
- Regulates libido & mood
Monitoring: Regular blood tests keep estradiol in the optimal range.


🔄 Thyroid Function (TSH, T3, T4)
TSH: Pituitary signal to thyroid T4: Inactive thyroid hormone T3: Active hormone regulating metabolism & energy
Why test with TRT:
- Symptoms overlap with low T
- Thyroid dysfunction impacts testosterone production & SHBG levels
- Full thyroid panel ensures accurate diagnosis before or alongside TRT
🛡️ Thyroid Peroxidase (TPO) Antibodies
Purpose: Diagnose Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (autoimmune hypothyroidism).
Why important:
- Identifies root cause of thyroid issues
- Confirms autoimmune condition
- Predicts future risk of hypothyroidism
- Guides treatment plan




